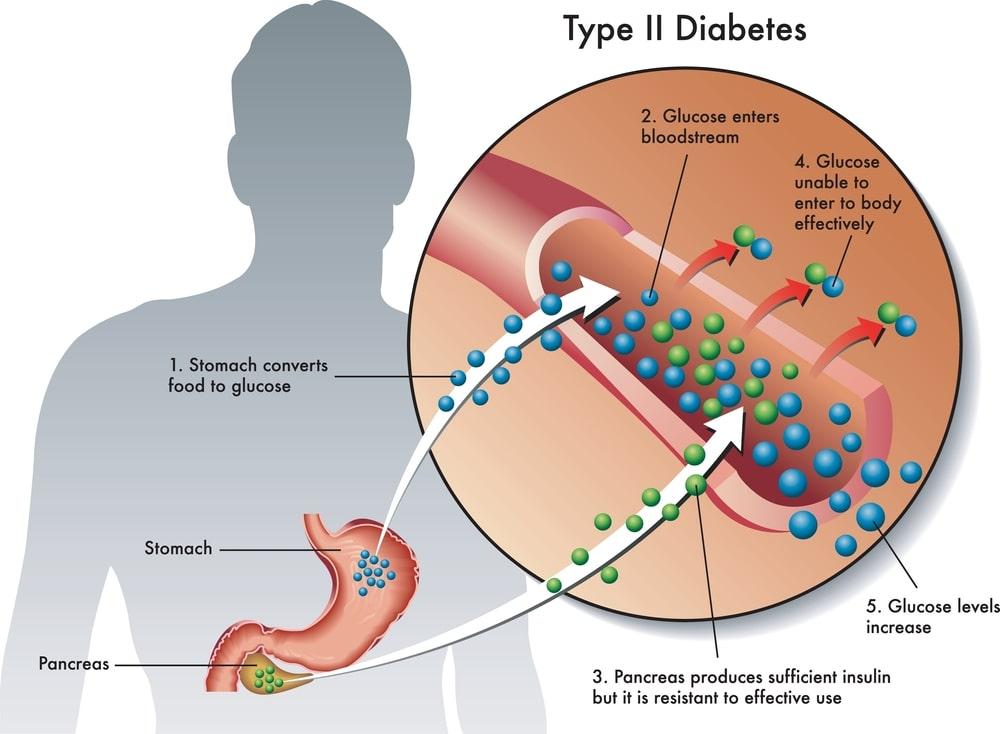
Type 2 diabetes (T2D) happens when our body doesn’t use insulin properly. Insulin is a hormone that helps our cells use glucose (sugar) from the food we eat for energy. But in type 2 diabetes, our cells become less sensitive to insulin, so glucose builds up in the blood.
To make up for this, our pancreas makes more insulin. But over time, it can’t keep up, and blood sugar levels rise. High blood sugar can hurt our body, causing problems like tiredness, blurry vision, and more infections.
If not controlled, type 2 diabetes (T2D) can lead to serious issues like heart disease, kidney problems, blindness, and nerve damage. Some people with type 2 diabetes may need insulin injections to manage their blood sugar levels.
Causes of Type 2 Diabetes (T2D):
Type 2 diabetes happens when your body doesn’t use insulin properly. This leads to high blood sugar levels because glucose can’t get into your cells. Over time, your pancreas can’t make enough insulin to keep up. This can cause health problems. It’s caused by a mix of genetics and lifestyle factors like diet, exercise, and high blood pressure. Some factors, like age or ethnicity, can’t be changed. But making healthy lifestyle choices can help lower your risk of getting type 2 diabetes.
Symptoms of Type 2 Diabetes (T2D):
Type 2 diabetes can sometimes sneak up on people without causing any noticeable symptoms, or the symptoms may be so mild that they go unnoticed. Because the signs can appear gradually, some folks may have type 2 diabetes for years before finding out they have it.
But even if you don’t feel anything unusual, there are a few things your body might be trying to tell you that could point to high blood sugar levels, which could mean you have diabetes. These signs include:
- Fatigue
- Constant hunger
- Blurred vision
- Frequent infections
- Sudden, unexplained weight loss
- Excessive thirst and increased urination
- Numbness, tingling, or pain, primarily in the legs, feet, hands, and arms
- Sores or cuts that heal slowly or do not heal
Diagnosis of Type 2 Diabetes (T2D):
To find out if someone has type 2 diabetes, doctors use tests to measure their blood sugar levels. They might use one or more of these tests to make a diagnosis. These tests are simple and help doctors figure out if someone has diabetes. They include:
- Fasting blood glucose test – a blood glucose level of 126 mg/dl or higher is considered diabetes
- Hemoglobin A1C test – a level of 6.5 percent or higher is considered diabetes
- Oral glucose tolerance test – this test is mostly considered to diagnose gestational diabetes; doctors measure the results of this test differently depending on whether you are being tested for T2D or gestational diabetes
- Random blood glucose test – a blood glucose level of 200 mg/dL or higher is considered diabetes
Getting tested for diabetes is easy and usually done at your doctor’s office or a lab. If your test shows that your blood sugar level is high, your doctor may ask you to take another test on another day to double-check and make sure of the diagnosis.
Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes (T2D) with Semaglutide:
Type 2 diabetes, a chronic condition characterized by high blood sugar levels, can be effectively managed with medicines like Semaglutide. As a glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1 RA), Semaglutide helps regulate blood sugar levels by mimicking the action of a naturally occurring hormone called glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1). By stimulating insulin secretion, suppressing glucagon secretion (which increases blood sugar levels), slowing gastric emptying, and promoting feelings of fullness, Semaglutide improves insulin sensitivity and reduces blood sugar levels in individuals with type 2 diabetes.
Clinical studies have demonstrated the efficacy of Semaglutide in improving glycemic control and reducing the risk of diabetes-related complications. Additionally, Semaglutide has been shown to promote weight loss, making it particularly beneficial for overweight or obese individuals with type 2 diabetes.
Along with lifestyle modifications such as dietary changes and increased physical activity, Semaglutide plays a crucial role in the comprehensive management of type 2 diabetes, helping individuals achieve better blood sugar control and reducing the risk of long-term complications associated with the condition.
References:
https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/basics/type2.html